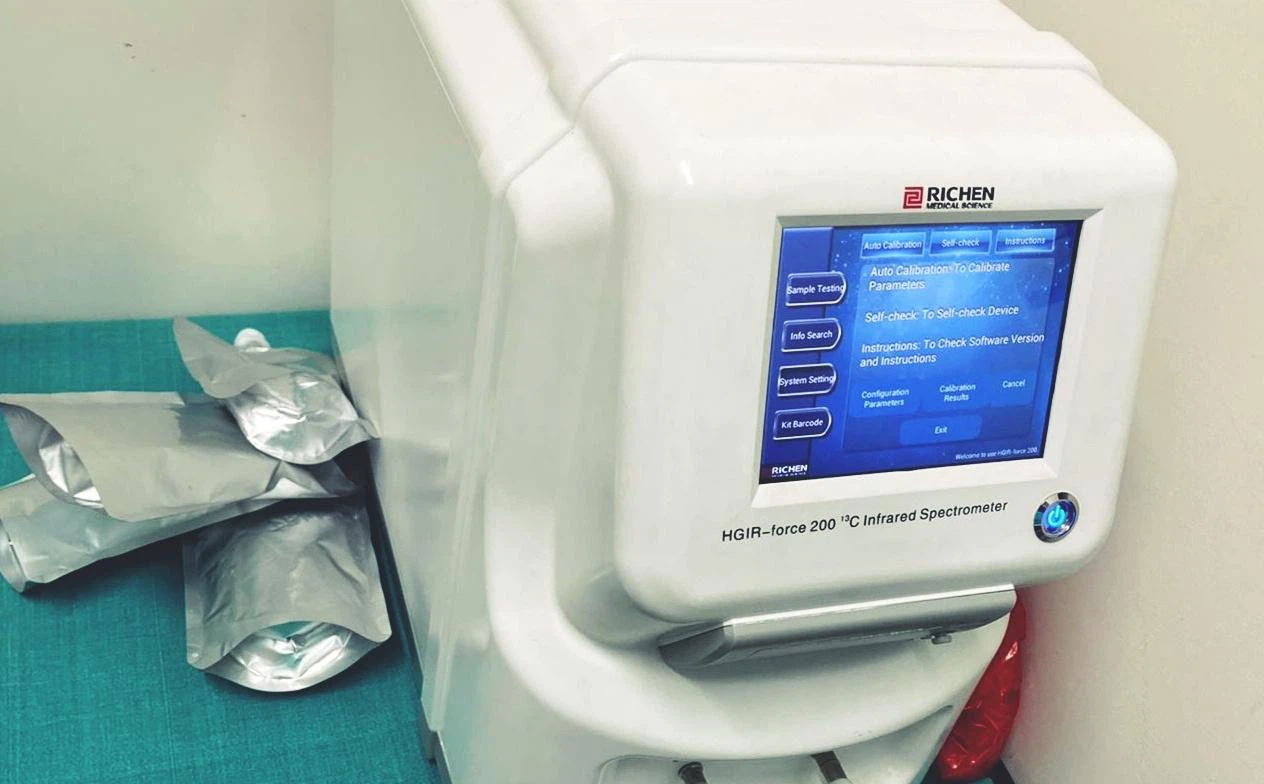
13C is a non-radioactive isotope that can be used safely for repeated testing, which is frequently required in clinical practice, and for detecting H pylori infection in children and women of childbearing age.
 Furthermore, 13C-urea has been the most widely used substrate in methodological studies performed to validate this kind of diagnostic test. Another relevant advantage of using the stable isotope is that breath samples can be sent by post or courier to remote analysis centres, thus promoting the distribution of the test, which can even be performed at home if the patients are adequately selected and instructed.
Furthermore, 13C-urea has been the most widely used substrate in methodological studies performed to validate this kind of diagnostic test. Another relevant advantage of using the stable isotope is that breath samples can be sent by post or courier to remote analysis centres, thus promoting the distribution of the test, which can even be performed at home if the patients are adequately selected and instructed.
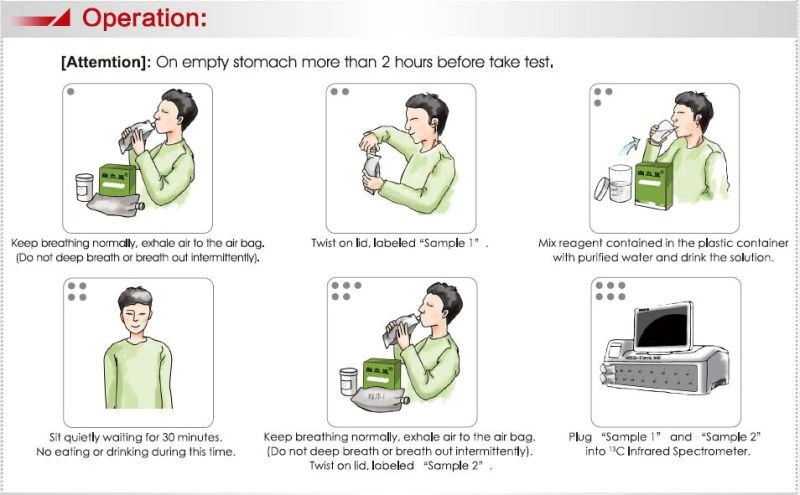
Urea C-13 is a radiolabelled urea molecule used to diagnose stomach ulcers caused by Heliobacter pylori. In the presence of H. pylori, urea C-13 is metabolized by urease to produce ammonia and 13c carbon dioxide at the interface between the gastric epithelium and lumen. The radioactive carbon dioxide is absorbed in the blood and is detected when exhaled in the breath.
The 13C-UBT is a simple and innocuous assay which requires only few precautions in order to obtain accurate results.
Richen products and urea breath test shown in ehibition

